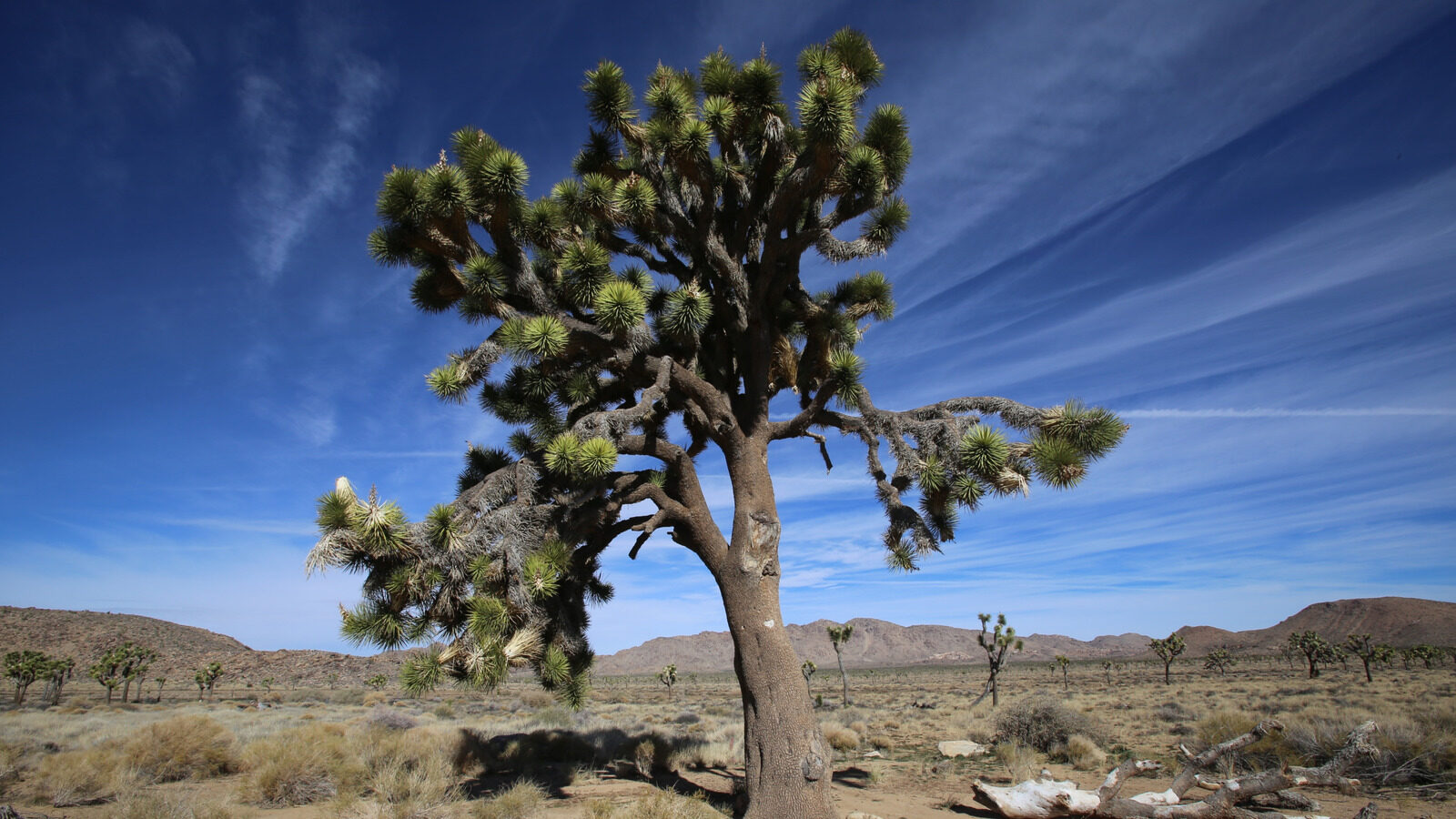
California’s Joshua trees are facing an unusual predicament that has scientists scratching their heads. The iconic flora, known for its unique appearance and resilience in arid conditions, has begun to bloom much earlier than expected. This phenomenon raises critical questions about the stability of their life cycle and the delicate balance within their ecosystem. Understanding what this means for the future of these trees is essential, especially in the context of climate change.
Understanding the life cycle of Joshua trees
The Joshua tree, a member of the Agave family, is not just another desert plant; it is an integral part of the Mojave Desert ecosystem. Typically, these trees bloom between February and May, a period when they rely on specific pollinators for successful reproduction. The flowers of the Joshua tree are specially adapted, being pollinated exclusively by two species of yucca moths. This relationship is a prime example of mutualism, where both species benefit from the interaction.
- Flowering Time: Joshua trees usually bloom in spring.
- Pollinators: Two species of yucca moths are essential for fertilization.
- Life Cycle: After pollination, the moths lay eggs in the flowers, which helps facilitate seed development.
- Environment: These trees thrive in dry, rocky soils, primarily in the Mojave Desert.
However, the synchronization between the Joshua trees and their pollinators is delicate. If the trees bloom early, as they have recently, the timing may not match with the moths’ hatching, resulting in missed opportunities for fertilization. This disruption can have cascading effects not just on the trees but on the entire ecosystem that depends on them.
The impact of climate change on Joshua trees
With climate change altering weather patterns and seasonal cycles, the early blooming of Joshua trees could be a direct result of shifting environmental conditions. A cooler, drier year followed by unexpected rainfall might have triggered this unusual flowering pattern, as suggested by researchers. Understanding these impacts is crucial for conservation efforts.
- Temperature Changes: Fluctuations in temperature can affect blooming times.
- Water Availability: Irregular rainfall patterns influence plant health and flowering.
- Habitat Loss: Urban development and climate stressors reduce available habitats for these trees.
Scientists are alarmed by the potential long-term consequences of such changes. Joshua trees are already classified as a sensitive species, and their survival is at risk as they may not adapt quickly enough to the rapid changes in their environment.
Citizen science: a collaborative approach to research
In an innovative move, researchers at California State University Northridge are tapping into the power of citizen science to gather data on the Joshua trees. They are inviting the public, particularly those in or visiting the Mojave Desert, to participate actively in monitoring these plants.
- Photo Documentation: Citizens are encouraged to photograph any Joshua tree flowers or fruit they encounter.
- Data Sharing: Participants can upload their observations to the iNaturalist app, creating a valuable database for researchers.
- Community Engagement: This initiative fosters a sense of community and shared responsibility for local ecosystems.
This grassroots approach allows scientists to gather a wealth of data points, which can then be analyzed alongside environmental factors such as weather patterns and temperature changes. By using machine learning models, the researchers hope to predict future blooming cycles, providing vital information for conservation strategies.
Research findings and future implications
While the exact triggers for the anomalous blooming are still under investigation, there are hypotheses based on previous research. For instance, an earlier anomalous bloom in 2018 was linked to environmental conditions similar to those experienced recently. By understanding the interplay between climate variables and blooming patterns, scientists can make more informed predictions about the future of the Joshua tree population.
| Year | Blooming Pattern | Environmental Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | Anomalous Bloom | Cool, dry year with intense rainfall |
| 2025 | Early Bloom | Similar weather conditions observed |
This research is crucial not only for the Joshua trees but also for the various species that rely on them. The ongoing study might inform broader ecological conservation efforts, helping to preserve not just this iconic tree but also the diversity of life it supports.
 Uninhabited Islands: Exploring Worlds Without People
Uninhabited Islands: Exploring Worlds Without PeopleThe role of conservation in protecting Joshua trees
As the climate continues to change, proactive conservation measures become increasingly essential. Protecting Joshua trees involves not only understanding their reproductive cycles but also managing their habitats effectively.
- Habitat Preservation: Protecting the Mojave Desert’s ecosystem is vital for the survival of Joshua trees.
- Research Funding: Increased funding for ecological research can advance our understanding of these trees.
- Public Awareness: Educating the community about the importance of Joshua trees can foster support for conservation efforts.
By involving the public in data collection and raising awareness about the significance of these trees, conservationists can work towards ensuring a future where Joshua trees continue to thrive in their natural habitat.