As the world grows increasingly interested in foraging and natural foods, the dangers associated with wild mushrooms are often overlooked. The recent surge in mushroom poisonings in California serves as a stark reminder of the risks involved. Understanding these risks is essential not only for foragers but also for anyone who enjoys the outdoors.
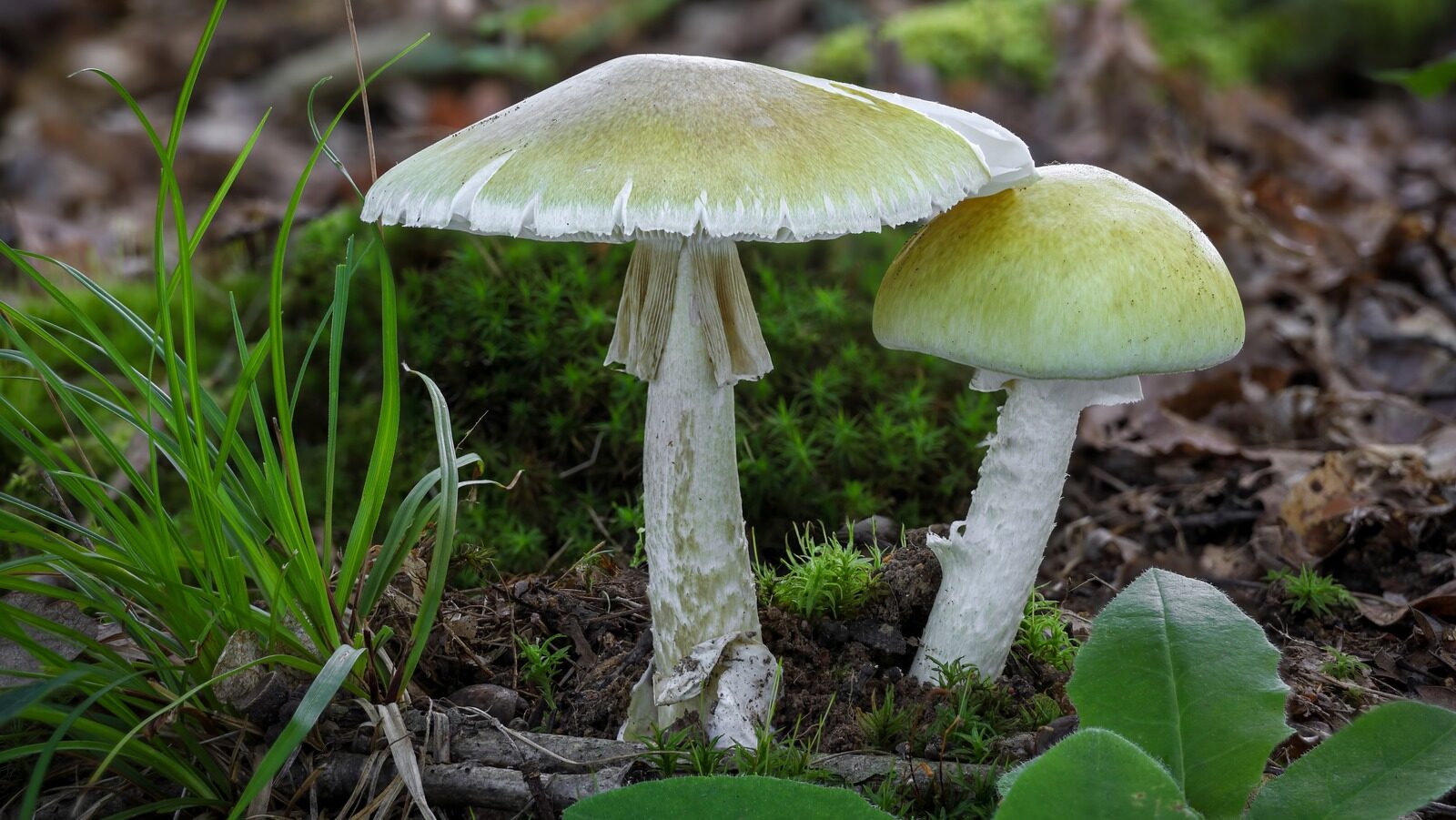
In the heart of Northern California, health officials are raising urgent alarms regarding a significant outbreak of mushroom poisoning. As of the latest reports, 35 people have been hospitalized, three individuals have undergone liver transplants, and tragically, three have lost their lives. This alarming spike in cases stands in stark contrast to the typical annual figures, where fewer than five cases are reported in California. The cause of this outbreak? An unusually wet season has created ideal conditions for the growth of toxic mushrooms, particularly the notorious death cap mushroom.
Understanding the mushroom poisoning outbreak in California
The current outbreak is a result of several months of consistent rainfall, which has saturated the soil and allowed for extensive mushroom growth across regions like the San Francisco Bay Area. This has attracted many enthusiastic foragers who, despite their best intentions, may not possess the necessary knowledge to identify dangerous species.
Among the most perilous mushrooms is the death cap (Amanita phalloides), which has been identified in multiple counties, including:
- San Francisco
- Alameda
- Contra Costa
- San Mateo
- Santa Clara
- Monterey
- Santa Cruz
- Sonoma
Health officials are urging the community not to consume any wild-foraged mushrooms, emphasizing that even experienced foragers can misidentify edible mushrooms, putting themselves at significant risk.
Why you should never eat wild mushrooms
While there are numerous resources available that claim to offer foolproof methods for distinguishing between edible and poisonous mushrooms, the reality is much more complex. If you value your health and safety, it is crucial to avoid consuming any mushrooms that you have foraged yourself.
Even seasoned mushroom hunters can easily mistake the deadly death cap for more common edible varieties such as field mushrooms or straw mushrooms. The danger lies in the presence of amatoxins, lethal compounds that can cause severe harm even in minute quantities. The symptoms of poisoning can take several hours to manifest, leading to a false sense of security for those who have ingested these dangerous fungi.
The deadly effects of amatoxins
Amatoxins are a group of cyclic peptides that disrupt cellular processes, particularly affecting the liver and kidneys. The timeline of symptoms following ingestion typically unfolds as follows:
- Initial Phase: Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and severe abdominal pain may begin within 6 to 24 hours.
- False Recovery: After the initial wave of symptoms subsides, the victim may feel temporarily better, leading to a dangerous sense of relief.
- Severe Damage: Within days, liver and kidney functions decline rapidly, often requiring urgent medical intervention such as a liver transplant.
Without timely treatment, amatoxin poisoning can lead to severe complications and even death. The physiological effects are brutal, often including delirium, diarrhea, and intense discomfort, making it a highly distressing way to suffer.
 Manson Family Members Today: Where Are They Now?
Manson Family Members Today: Where Are They Now?The importance of proper mushroom identification
Given the potential dangers, it is crucial to understand the differences between edible and toxic mushrooms. Some of the most common edible mushrooms, such as chanterelles or porcini, can be easily confused with their poisonous counterparts. Here are some tips for safer foraging:
- Always consult a trusted field guide or an expert before consuming any foraged mushrooms.
- Attend workshops or foraging tours led by experienced mycologists to learn about local species.
- Be mindful of local regulations regarding foraging, as some areas may have restrictions.
Education plays a vital role in preventing mushroom poisonings. By learning about the various species and their habitats, foragers can significantly reduce their risk of encountering toxic mushrooms.
Responsible foraging practices
Foraging can be a rewarding and sustainable practice when done responsibly. If you are interested in harvesting wild mushrooms, consider these best practices:
- Only harvest mushrooms that you can positively identify as safe.
- Avoid areas near roads or polluted sites, as mushrooms can absorb harmful substances from their environment.
- Limit your gathering to what you will consume, allowing the ecosystem to thrive.
Responsible foraging not only ensures your safety but also contributes to the health of local ecosystems. Mushrooms play essential roles in nutrient cycling and soil health, and removing too many can disrupt these processes.
Conclusion: Awareness is key
The recent mushroom poisoning outbreak in California highlights the importance of awareness and education surrounding wild mushrooms. With the right knowledge, foragers can enjoy the benefits of foraging while minimizing risks. Always prioritize safety and never hesitate to seek help or advice from experienced individuals in the field.